Emergencies
This is a significant aspect of our work. The clinic offers a a 24/7 service for emergencies.
We are on call at the number 051 6920701
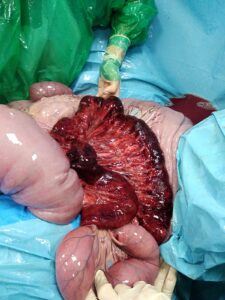
Colic represents the most frequent emergency in equine practice. Most of the cases are evaluated and then referred by colleagues. Information on patient’s condition, therapies, transport times is collected by telephone to better prepare the patient’s hospitalization.
After a complete set of examinations procedures and laboratory exams, it is decided whether the case is of medical or surgical relevance. In the latter case, the horse is moved to the surgical theatre dedicated to abdominal surgery, where the anesthesia apparatus and monitoring systems are ready.
The operated patients after surgery follow a routine similar to medical cases, with 24/24 hours monitoring and regular checks (clinical examinations, ultrasonographic control, lab tests and therapies). The hospitalization of a horse after colic surgery averages 8-14 days.
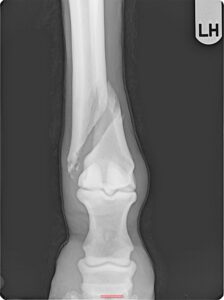
Fractures represent the main orthopedic emergency. First aid by the referring veterinarian is paramount: diagnosis of the fracture, a correct immobilization of the involved limb and patient’s stabilization for transportation under optimal conditions are crucial procedures for a successful outcome.
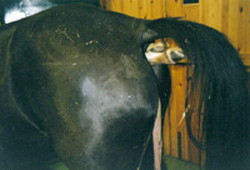
Septic arthritis and tenosynovitis both in the neonatal foal and in the adult horse represent other orthopedic emergencies. Laminitis, although rare in recent years, is another challenging condition. Wounds, particularly large deglowing wounds of the distal limb, frequently need hospitalization for a better treatment.
Late term pregnant mares may be affected by dystocia and in this case the most successful treatment is represented by emergency cesarean section.
Surgery
Surgery represents a significant portion of our activity. It mostly consists of elective surgery. Surgeries are performed under general anesthesia in most cases and rarely, when possible, in the standing horse.
The most common procedures in orthopedic surgery are diagnostic and surgical arthroscopy mostly for osteochondrosis and chip fractures and tenoscopy for superior check ligament desmotomy, desmotomy of the fetlock annular ligament.
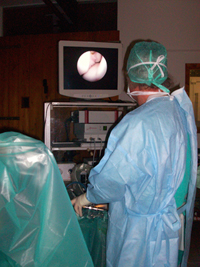
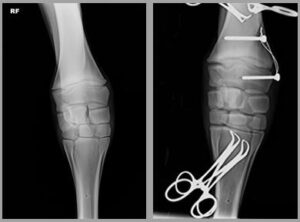
Orthopedic surgery also includes neurectomy (for palmar foot pain of proximal suspensory desmitis), surgery for angular limb deformities in the foal, splint bone ostectomy, internal fixation for fractures (mostly proximal phalanx, metacarpal/tarsal condyles, third carpal and tarsal bones, olecranon) and surgical arthrodesis.
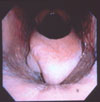
Soft tissue surgery includes surgery of the upper respiratory tract, urogenital surgery (castration, cryptorchidectomy, ovariectomy), umbilical herniorraphy, surgery for ruptured bladder and umbilical infections in the foal.