Post partum uterine rupture
6 year old Standardbred mare
History
The mare was admitted with signs of colic of 5 hour duration. The mare delivered a normal foal 20 hours before and expelled the full placenta after 7 hours.
Clinical examination and lab tests
The mare was in good bodily condition, with moderate pain, the attitude was depressed and she was nearly indifferent to the foal.
Heart rate was 52 bpm, respiratory rate 16 bpm, with absence of peristalsis on both sides of the abdomen. Rectal temperature was 38.2°, mucosal congestion was visible, with increased capillary refill time. PCV was 52%, total protein 6.8 g/dl and leucocytes 2500/mm3. Blood gas analysis showed pH 7.33 and excess base – 3.4 mmol/l.
No consistent findings were appreciated by rectal palpation, with the exception of edematous large colon. Transrectal and transabdominal ultrasonography were negative.
Gastric reflux was absent.
The mare was kept under observation. Two hours later the clinical pattern worsened, WBC dropped to 2300/mm3, HR increased to 64 bpm and the mare showed pain, with pawing and tendency to lie down. The mare was submitted to exploratory laparotomy.
Surgical treatment
The mare was premedicated with xylazine 0.8 mg/kg and anestesia was induced using guaifenesin in 6% solution and ketamine 1.8 mg/kg. Inhalation anesthesia was maintained with isofluorane vaporized by N2O and oxygen.
When the abdominal cavity was entered, the peritoneal fluid appeared sanguinolent. Small and large intestine, despite not fully exposed, appeared normal. Examination of the uterus showed a full thickness rupture of a uterine horn (Figure 1).
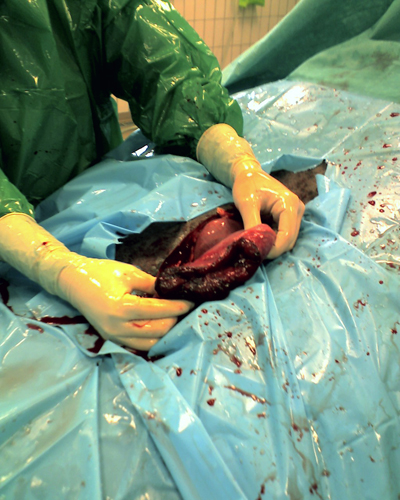 Fig.1
Fig.1
The rupture was repaired with a two-layer suture (apposing suture on mucosa and muscular layer, inverting suture on serosa). After large flushing of the abdominal cavity, the surgical wound was sutured in three layers.
Recovery time was short and the mare was able to stand after 10 minutes, when she was returned to the stall and joined the foal. The mare was kept under antibiotics (gentamicin 6.6 mg/kg, procain penicillin 22.000 UI/kg) for 5 days.
Postoperative management and follow up
The mare recovered normal behaviour with the foal, with absence of pain.The mare was treated with flunixin meglumide 1.1 mg/kg and prednisolone. All blood parameters returned to normal values in a few days and only the third and fourth days post-op the mare showed a mild increase of body temperature (38.9°). The mare was dismissed after 13 days of hospitalization. In the same season, she became pregnant and delivered a live foal the next season.
Comments
Post partum colics represent a special condition of the mare. The causes include, other than small and large intestinal problems, specific condition like rupture of the caecum, rupture of the uterine artery and uterine tears.
